3. Introduction to China’s AI computing power development strategy (2) _ “8. Regional development of AI”
- Oct 16, 2024
- 6 min read


In 2017, China developed a comprehensive strategy to establish itself as a global leader in artificial intelligence. This strategy is built on six key pillars:
1. Legal and ethical framework: China aims to create a sound legal and ethical framework for the development and application of AI. This includes establishing legal regulations for AI development and addressing civil and criminal liability, privacy and intellectual property issues. It will also focus on AI behavioral science and ethics.
2. Policy support: The government provides policy support for the development of AI, especially for SMEs and start-ups. Financial incentives, such as tax exemptions and R&D deductions for high-tech companies, have also been introduced to promote AI innovation. In addition, data sharing and protection policies are also being strengthened.
3. Standardization and intellectual property: China seeks to take the lead in AI technology standards and rights by establishing an AI standards framework for security, usability, interoperability, and traceability. It encourages Chinese AI companies to participate in and develop international standards and strengthen AI-related intellectual property protection.
4. Security and Regulation: The Chinese government has studied the impact of AI on national security and confidentiality, developed AI security standards and assessment systems, developed security precautions, and created a monitoring system to track the development of AI technology. China emphasizes the importance of preventing risks and managing data abuse, privacy infringement, and unethical behavior.
5. Workforce training: Another priority is preparing the workforce for the impact of AI. China is studying the changes in employment structure and new skills required due to AI. Efforts include establishing a lifelong learning and employment training system, focusing on AI skills training in educational institutions, and encouraging programming education.
6. Popularization of AI: China is promoting the widespread adoption of AI through educational programs, curriculum integration, and public outreach activities. This includes introducing AI-related courses in schools, promoting programming education, and encouraging AI competitions and creative activities to enhance the public’s understanding and use of AI.
China’s strategy demonstrates its commitment to harnessing the potential of AI for economic and technological growth, while emphasizing the importance of ethical, safety, and comprehensive policy measures.
Main Participants
Since AlphaGo defeated Lee Sedol in 2016, China has become an important player in the development of artificial intelligence and is gradually approaching the level of the United States.
In 2022, China's total private investment was $13.4 billion, which is still significantly behind the United States, but ahead of other countries. Technology giants such as Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, Huawei and iFlytek remain important players in the field of artificial intelligence.
However, the main impetus comes from the Chinese government, which has provided substantial political and economic support to strategically important industries such as AI through subsidies that distribute cash to technology startups through competitions organized by public-private partnership platforms such as the Artificial Intelligence Industry Alliance (AIIA).
For example, Chinese AI startup iDeepWise received a cash prize of approximately $75,000 and a $3 million R&D grant after winning the AIIA competition in 2018. Public-private investment funds such as the Government Guidance Fund are an additional mechanism for the Chinese government to inject capital into emerging technologies such as AI. By 2022, more than 2,100 such funds were reported to have been established, raising nearly $940 billion.
The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) of China appears to be on par with the Pentagon in terms of military investment. If public contracts are any indication, the PLA invests more than $1.6 billion per year in AI systems. However, this does not reflect actual numbers, as most of the investment is likely focused on R&D projects, and most resource-intensive projects are classified.
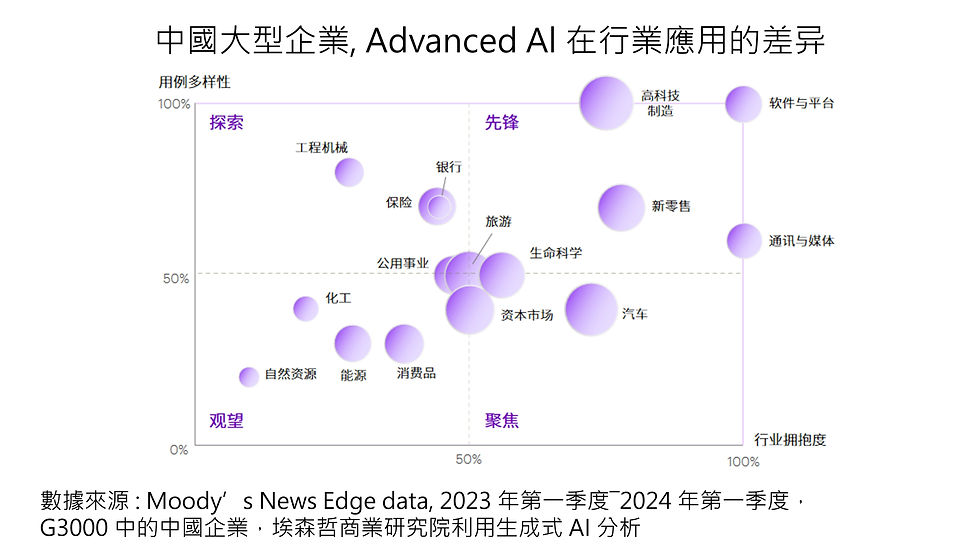
Industries that widely use Ai:
Software and platform, communications and media, high-tech manufacturing, new retail and other industries
Ai is widely used in customer operations, such as content generation, personalized marketing, and intelligent customer service. The generative approach can quickly generate innovative and practical ideas, and therefore is widely used in the above industries.
"Focus" on industries that apply Ai:
Automobile, pharmaceutical and other industries
Ai focuses on product research and development, product intelligence, etc.
In the automotive industry, Ai is used in the areas of autonomous driving and smart cabins.
Leading pharmaceutical companies have invested heavily in generative AI to accelerate the efficiency of new drug research and development.
「Explore」 Industries where Ai is applied:
Construction machinery, insurance, banking, etc.
Ai is used in many application scenarios, but the depth of use is relatively shallow.
CATL is actively deploying generative AI technology in new battery material research and development, defect inspection and other intelligent manufacturing fields
In the banking industry, some large banks have already applied large language models to scenarios such as knowledge question and answer, marketing customer service, investment research, and risk management.
"Wait and see" Ai application industries:
B2B asset-intensive industries, such as resources, energy, and chemical industries, etc.
The application of AI is relatively lagging behind.
Enterprises are more concerned about manufacturing and supply chain efficiency because they are bound by safety production and compliance.
These industries are relatively cautious in their application of AI, and the disclosure of use cases is relatively minimal.

1. Distributed development of multiple independent AIs, with negative impacts:
Waste of resources
In order to adapt to various scenarios, multiple independent AIs are developed, and there is a lack of coordination between systems.
→ Increase maintenance costs
→ Increase manpower expenses
Data cannot be communicated
AI cannot fully analyze across departments
→ Decreased forecast accuracy
Increased safety risks
Data is stored and processed in multiple locations.
→ Increased risk of data breach and abuse
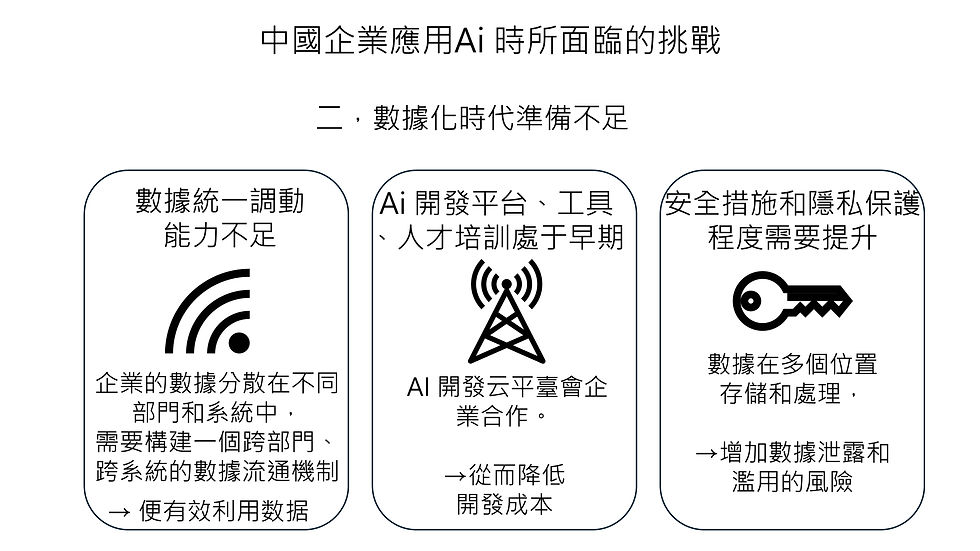
Second, we are not prepared for the digital age
Insufficient data unification and mobilization capabilities
The enterprise's data is scattered in different departments and systems, and it is necessary to build a cross-departmental and cross-system data circulation mechanism
→ Effective use of data
Ai development platforms, tools, and talent training are in the early stages
AI development cloud platform will cooperate with enterprises.
→Thereby reducing development costs
Security measures and privacy protection need to be improved
Data is stored and processed in multiple locations.
→ Increased risk of data breach and abuse

3. Adjustment of corporate structure and work model
As AI capabilities continue to approach human levels and are applied to all kinds of life and work scenarios, the way we work as we know it today is likely to undergo tremendous changes.
China's retail, life sciences, high-tech, and energy industries have the potential to optimize or automate more than 40% of their work time with generative AI.
Employees with weak digital skills, less work experience, and lower education levels are
The likelihood of a shock is greater and the risk of a worsening digital divide is rising.

1. Establish a unified AI data allocation mechanism system
AI can create value in multiple dimensions, such as automation, shared services, new ways of working, diversified workforce models (such as outsourcing), resource optimization, etc.
Gaining a holistic perspective requires breaking down functional and departmental barriers, as siloed operations hinder progress and create friction, which in turn affects decision-making and productivity.
Unified data architecture and cross-functional teams can help companies reposition their organizations.
Build end-to-end business and decision-making capabilities to identify opportunities in the value chain and open up new value pools.

Second, increase investment in "strategic AI"
Most companies have adopted a “conservative investment” approach, focusing on proven generative AI applications and achieving early results in functional departments such as IT, marketing, finance, and customer service.
Use cases in these areas include supporting code writing, content creation, automated financial reporting, knowledge retrieval, improving customer service efficiency, and more.

While the cost of deploying AI at scale within an enterprise is high, the opportunity cost of waiting may be even more expensive. When deciding where to deploy generative AI, enterprises need to take a value-led approach.
- In which areas can the application of full consideration of costs and returns create differentiated competitive advantages for enterprises?
- After comprehensively considering supplier costs and manual supervision costs, what is the unit economic benefit of technology application?
- How much change will it cause?
-Are the relevant risks controllable?

The emergence of generative AI has brought new requirements to the digital core of enterprises, including the need for new types of data, the choice of models, and increased computing costs.
Combined with what has been mentioned above, Chinese enterprises do not have a solid foundation in digital technology, the degree of data circulation and the proportion of cloud computing are not high, and IT security deployment is insufficient.
Therefore, Chinese companies need to accelerate the construction of digital cores while balancing innovation investment.
.jpg)































Comments