3. Generalist vs. Specialist Models in AI "1. AI Algorithm Characteristics"
- Oct 16, 2024
- 1 min read

"General-purpose large models lack specialized knowledge in specific domains, which necessitates training industry-specific large models that are closely integrated with business systems to achieve actionable intelligent applications. Additionally, many enterprises have proprietary data that cannot be disclosed externally, such as customer information and interaction behavior in finance and healthcare. Therefore, there is a need for private training and localized deployment of large models.

"The models require further stratification, such as L0-L1-L2 levels, progressing from basic models to vertical models and eventually to domain experts, in order to gradually enhance specialization. Vertical domain models involve the incorporation of specific training data, accounting for about 10-15% of the pre-training ratio, to produce industry-specific large models.
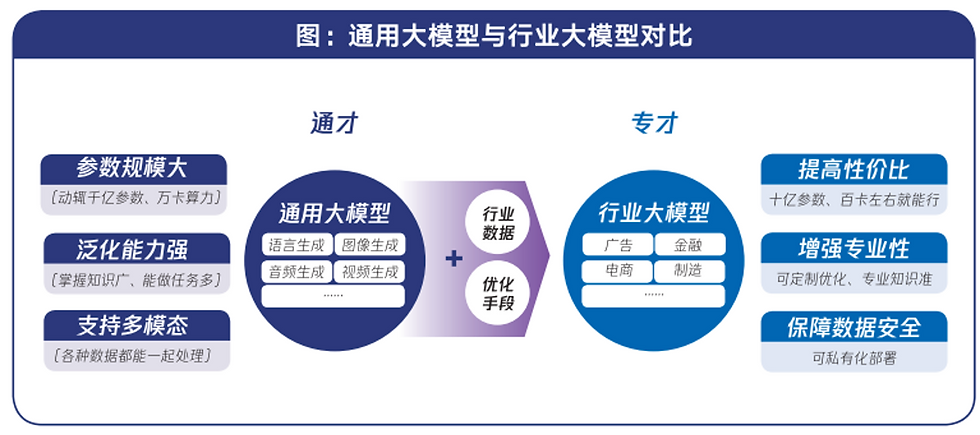
1. High Cost-Effectiveness
Industry-specific large models can achieve better performance based on smaller parameter models through relatively low-cost retraining or fine-tuning.
Industry-specific large models with parameter counts in the billions to tens of billions are currently the mainstream choice, significantly saving development costs compared to general-purpose large models, which often exceed hundreds of billions of parameters.
2. Customizable Specialization
Industry-specific large models can be developed based on open-source models, allowing for adjustments to model structure and parameters as needed to better fit personalized application requirements.
Through the Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) approach, organizations can quickly select suitable models from various options available on the platform, including initial versions of industry-specific large models already developed by vendors.
3. Data Security and Control
Industry-specific large models can be deployed privately, enabling organizations to utilize proprietary data more confidently to enhance application effectiveness while reducing concerns about data security.
.jpg)



Comments